Tersan’s KEM® explainable AI:
The next stage of human machine collaboration AI
which learns and explains why
The next stage of human machine collaboration AI
which learns and explains why

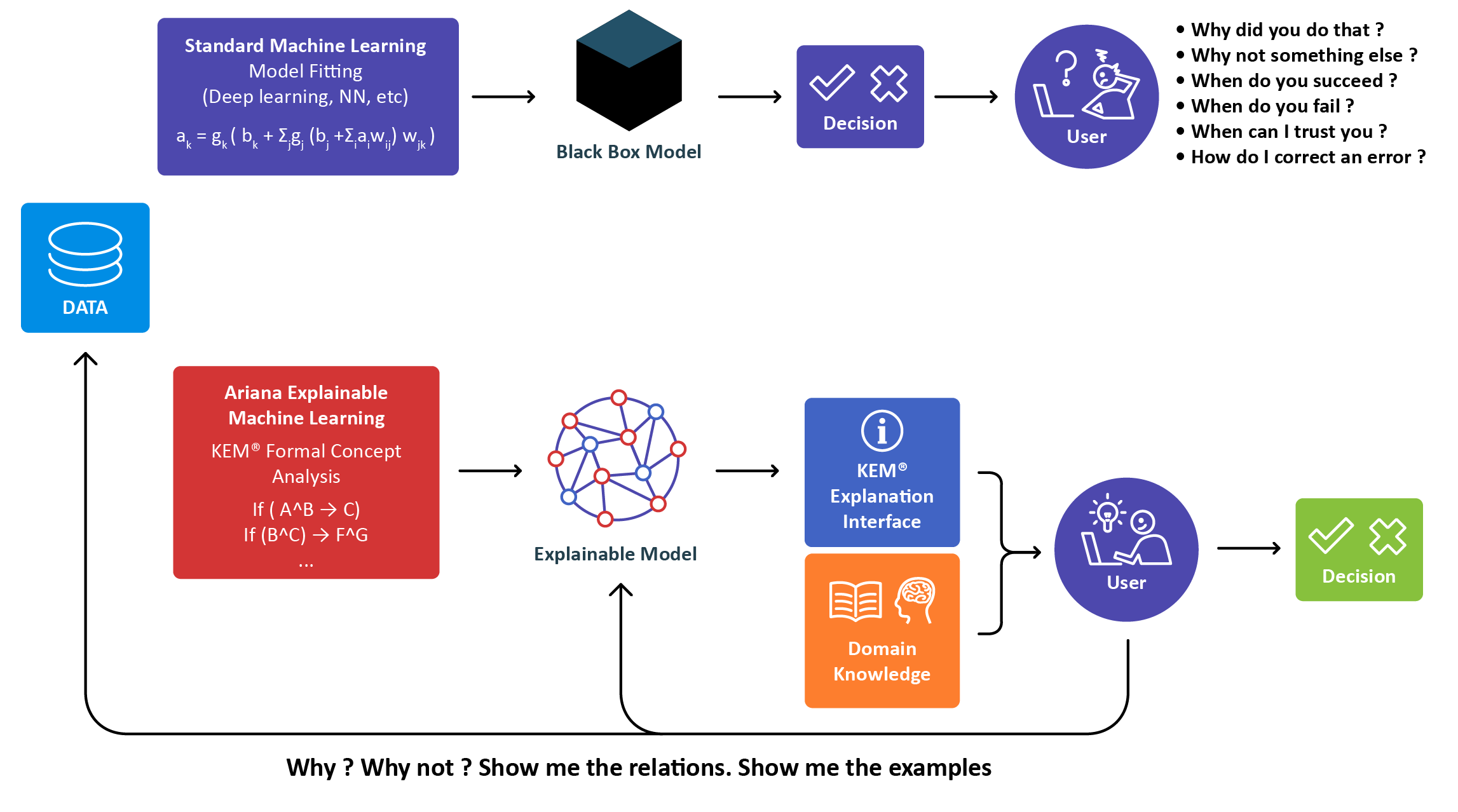
Tersan Pharmaceuticals Ltd has developed KEM® (Knowledge Extraction and Management) the most advanced Explainable Artificial Intelligence platform based on Galois Lattices (also known as Formal Concept Analysis or FCA).
KEM® uses association rules to fully explore complex datasets in order to reveal hidden relationships and to derive new hypotheses.
Tersan’s eXplainable Al reduces billions of relations into a few implications that can be challenged by humans.
KEM® is the result of over 15 years of development for the life sciences at Tersan by experts in Machine Learning, Statistics, Biology, biomarker research and drug development.
Our XAI technology uncovers hidden signals and complex relationships that conventional statistical analyses
miss. It’s a unique approach that is both complementary to and supported by statistical analyses, guaranteeing
robust, reproducible results. We can easily analyze complex combinations of data including clinical, imaging,
metabolic, biochemical and NGS/omics.
Using existing and new data provided for your clinical trial, Tersan combines baseline characteristics, gene expression, protein measurements, matebolimic date. We generate all logical signatures, evaluate each to deliver signatures you can count on and ranks each combination of these data points showing you the most
important to your trail.
“Tersan®: The Explainable Artificial Intelligence Driven Precision Medicine Company “
With KEM®, the signatures are easily interpretable
Compared to other methods, KEM® is less sensitive to dataset imbalance in terms of positives vs. negatives, or in situations where the number of descriptors exceeds the number of samples by orders of magnitude (a common problem in clinical and biomarker datasets).
The KEM® approach identifies all possible signatures. The ranking and filtering are performed explicitly based on classification performance, signature simplicity (length), as well as any additional criteria such as biological knowledge (pathways enrichment) or clinical relevance (targeting specific patient subgroups) etc.
The KEM® approach identifies all possible signatures. The ranking and filtering are performed explicitly based on classification performance, signature simplicity (length), as well as any additional criteria such as biological knowledge (pathways enrichment) or clinical relevance (targeting specific patient subgroups) etc.
“Al Driven Knowledge Integration and Discovery Platform Aiming at Regulatory Strategy”
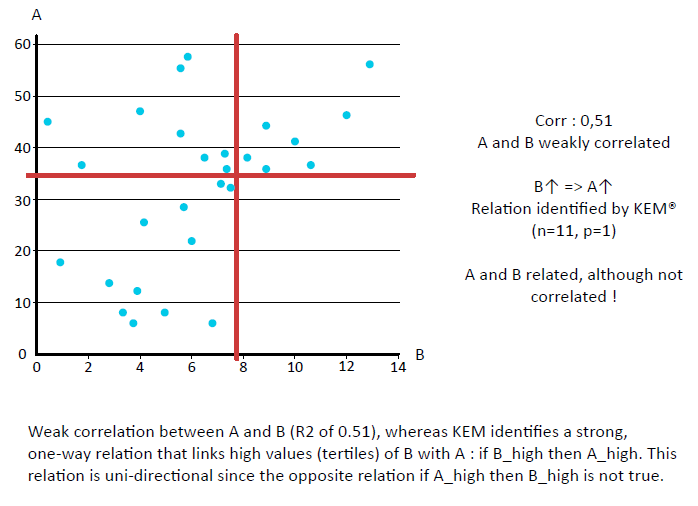
KEM® can identify all relevant relationships between variables
… even if only weakly correlated.

Traditional analytical approaches for the identification of multivariate classifiers often start with a univariate analysis on all features, the identification of markers that allow class discrimination, and the use of optimization algorithms such as Random Forest, SVM or Neural Networks to find the optimal combination of these markers.
KEM® uses FCA to extract significant associations between data in the form of uni-directional implications. All attributes (descriptors) in the data matrix are first transformed (or discretized) into binary variables. The discretization is based on either the data distribution or a semantic content (i.e. the thresholds are medically meaningful and actionable). Multiple binning schemes for each variable are considered.
In many cases, relations between variables often only exist within particular, specific ranges rather than globally. These relationships are frequently dismissed as weak correlations by more traditional approaches when, in fact, the relationships
are both relevant and meaningful.
KEM® delivers unsupervised, unbiased, total data exploration.
KEM® has its ability to identify relationships between descriptors, as opposed to between descriptors and endpoints only.
This strong implication is likely to be missed by standard, supervised methods. In addition, the analysis does not perform an optimization of the binning boundaries of descriptors towards a given endpoint (supervised).
This avoids many of the over-fitting issues, since there is no arbitrary optimization.
This can be compared with Random Forest, for example, where you may get rules that indicate that BMI should be < 17.003, which is unlikely to hold any medical meaning.
This avoids many of the over-fitting issues, since there is no arbitrary optimization.
This can be compared with Random Forest, for example, where you may get rules that indicate that BMI should be < 17.003, which is unlikely to hold any medical meaning.

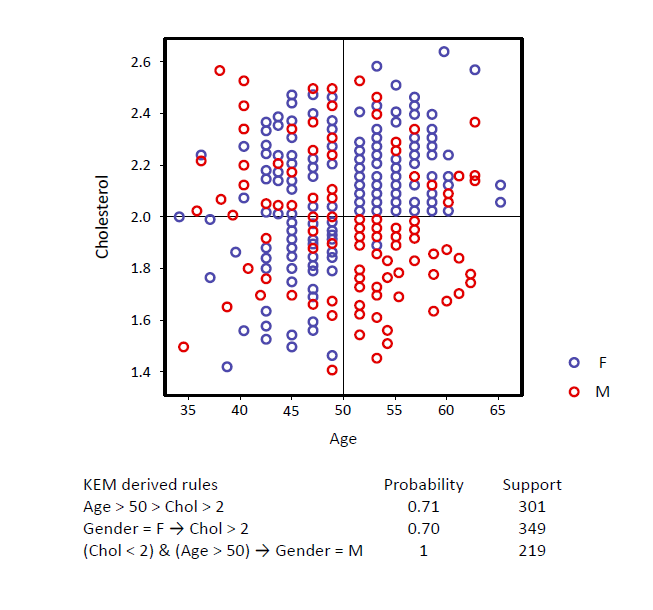
KEM® generates compact, interpretable signatures
with high specificity and sensitivity

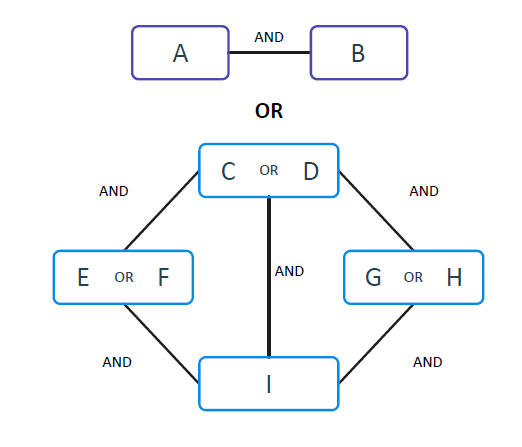
To generate signatures from the uncovered logical associations and perform class prediction, all equivalent combinations are first identified as “AND” clauses.
They contribute to the increase of the specificity of the signature. Multiple ANDs are then combined through OR clauses, increasing sensitivity. In the FCA paradigm, there is no need for global convergence; hence the system can identify multiple local minima that are connected via ORs, enabling the effective and efficient analysis of heterogeneous data. The signatures identified by KEM® are comprised of a non-linear combination of AND and OR functions. The result is usually a much more compact signature
They contribute to the increase of the specificity of the signature. Multiple ANDs are then combined through OR clauses, increasing sensitivity. In the FCA paradigm, there is no need for global convergence; hence the system can identify multiple local minima that are connected via ORs, enabling the effective and efficient analysis of heterogeneous data. The signatures identified by KEM® are comprised of a non-linear combination of AND and OR functions. The result is usually a much more compact signature
Latest Scientific Publications
Clinical Trials on Alzheimer's Disease
Conference (CTAD) 2020
” ANAVEX®2-73 (Blarcamesine) Currently in Phase 2b/3 Early)...
Pharmaceutical Users Software Exchange US 2020
“Artificial Intelligence ( AI ) Enhanced Precision Medicine Drug Development”
Clinical Trials on Alzheimer's Disease conference (CTAD) 2019, San Diego, USA
“Novel analytics framework for...
Clinical Trials on Alzheimer's Disease conference (CTAD) 2018, Barcelona, Spain
“Longitudinal 148-Week.

